The New York subway, locally known as “New York City Subway”, It is one of the most iconic and extensive underground transportation systems in the world..
Located in New York City, EU, This metro began operations on 27 October 1904, becoming a fundamental element in the daily life of the city and an icon of New York urban culture.
The system has 27 lines that intertwine throughout 472 stations, extending for a total of 399 kilometres (about 247.9 miles), making it not only one of the largest in terms of number of stations but also in service length.
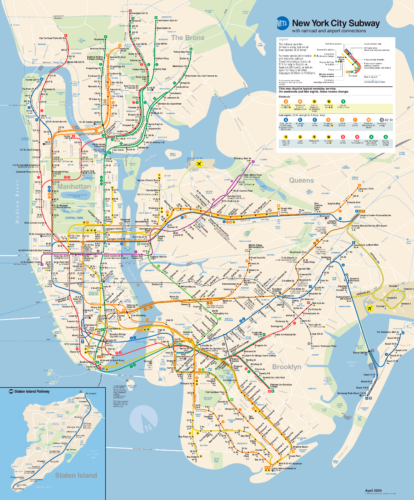
Here's the New York subway map:
Schedules
The New York subway operates 24 hours a day, 7 days a week. It's the city that never sleeps.
New York Subway Fares 2024
The subway system in New York, You have a variety of fare options for the 2024, suitable for both residents and visitors. Next, details of current rates and available options are presented:
Price list
- Travel fee (Pay-Per-Ride):
- $2.90 per trip: This is the standard fare for each trip on the subway and local buses.
- Single Ride Card: $3.25 for a unique trip, Available only at vending machines in subway stations.
- Unlimited Travel Cards:
- Card of 7 days: $34.00, offers unlimited rides on subways and local buses during 7 consecutive days.
- Card of 30 days: $132.00, allows unlimited travel on subways and local buses during 30 consecutive days.
- Card of 7 Express Bus Plus days: $64.00, includes unlimited trips on express buses, local and metro during 7 days.
- Reduced Rates:
- People older than 65 years and passengers with qualified disabilities can apply for reduced fares, which are the 50% of the base rate.
- AirTrain JFK:
- Unlimited Pass 30 days: $42.50, valid for unlimited rides on AirTrain JFK.
- Card of 10 trips: $26.50, Useful for those who frequent the AirTrain JFK.
Discounts and Additional Benefits
- OMNY: Contactless payment system that allows users to pay the basic fare and receive free transfers between metro and buses. Besides, si se pagan 12 trips in a week with the same device or card, additional trips within that week are free.
- Fair Fares NYC: A program that offers a 50% discount on subway and select bus fares for low-income New York residents.
Additional considerations
Users can pay their fares using the OMNY system with a contactless credit or debit card, a smartphone or wearable device (A physical card). This technology facilitates faster and more hassle-free access to the transportation system.
Official Web site
- This is the official website of the New York City Subway: MTA.
- This website has all attractions in New York.
History of the New York subway

Start and first phase (1904-1940)
The New York subway was inaugurated on 27 October 1904. Originally, the line operated from City Hall to 145th Street along the west side of Manhattan, what is now part of the IRT Broadway–Seventh Avenue line. This system was developed by the Interborough Rapid Transit Company (IRT).
In the following years, the system expanded rapidly. In 1913, was signed on “Dual Contracts”, an agreement that allowed the IRT and the newly formed Brooklyn Rapid Transit Company (BRT, más tarde Brooklyn-Manhattan Transit Corporation, BMT) expand your networks.
This led to expansion into Brooklyn and Queens., and new lines and services were created, such as the Astoria and Flushing lines that were inaugurated in the years 1910 y 1920.
Expansion and consolidation (1940-1968)
In 1940, the New York City government purchased the lines operated by the IRT and the BMT, integrating them into the New York City Transit Authority system, which would later become part of the Metropolitan Transportation Authority (MTA) in 1968. This change marked the beginning of an era of unification and standardization in services and rates..
After the Second World War, The subway began to suffer from a lack of funds for maintenance and expansion. Despite this, some major expansions occurred in this era, such as the extension of the IND Fulton Street line to Lefferts Boulevard in 1956 and the opening of the IND Rockaway line in 1956, that connected Manhattan to the beaches of Rockaway.
Modernization and renovation (1969-Gift)
Since the end of the years 60, The system has gone through several phases of renovation and modernization. The years 70 y 80 were particularly difficult, with crime problems and poor maintenance. Nevertheless, in 1982 A five-year renovation program was started with a budget of more than $1 billion, focused on improving the slopes, stations and signs.
One of the most significant projects in recent times was the opening of the Line extension 7 in Manhattan in September 2015, which added a station at Hudson Yards. Besides, the long-awaited Second Avenue Subway, whose construction began in earnest in 2007, inaugurated its first phase in January 2017.
History of the New York Subway Map
The history of New York City subway map design is marked by the contributions of various designers and different philosophies.
One of the most iconic designers was Massimo Vignelli, whose map “diagram style” of 1972 introduced a minimalist and abstract style. This map used bold colors and clean lines, favoring an easy-to-navigate layout to the detriment of geographic precision.
However, Vignelli's New York subway map design was controversial due to its lack of geographical fidelity, which led to debates within the design community (The seas).
In response to criticism of Vignelli's map, John Tauranac led the Metropolitan Transportation Authority Map Committee (MTA) at the end of the years 70. Tauranac favored a more geographically accurate map, which included more details about the city above the subway system. Their approach led to the development of a new map by Michael Hertz Associates, which was adopted in 1979 and has continued to evolve but is still in use today.
Previously, in 1955, Another notable contribution was made by George Salomon, who introduced an abstract approach inspired by Harry Beck's design for the London subway. Salomon's design was the first to systematize subway lines with a clear visual language, using 45° and 90° angles to simplify the complex network.
These designers and their maps have sparked ongoing debates about the balance between design simplicity and geographic accuracy., reflecting broader discussions in the field of graphic design about how to best convey complex information.
Each version of the New York City subway map has struck a balance between user experience and geographic representation, until you get to the current version.
Additional data
The New York subway is not only vital for daily mobility but is also an outstanding tourist and cultural attraction.
Near many of its stations are some of the most emblematic places in the city., like Times Square, Central Park and the Metropolitan Museum of Art. Besides, the system is known for its public art, with installations and murals that turn many of its stations into small art galleries.
Important Sites and Their Metro
These are the most notable sites:
- Times Square (Times Square – 42nd Street, N lines, Q, R, W, 1, 2, 3, 7, S). The nerve centre of the city, a meeting point for numerous subway lines and close to the famous lights and theaters of Broadway.
- Central Park West (59th Street Station – Columbus Circle, lines A, B, C, D, 1). Near the southwest entrance to Central Park, This station is an ideal starting point to explore the park and its surroundings.
- Wall Street (Wall Street Station, lines 2, 3, 4, 5). Located in the heart of the financial district, This station serves those visiting or working in the city's financial center.
- American Museum of Natural History (81st Street Station – Museum of Natural History, B lines, C). This station is decorated with museum themes and provides direct access to one of the most famous museums in the city.
- Museo Guggenheim (86th Street Station, Q line). Next to the iconic museum designed by Frank Lloyd Wright, This station is a hotspot for lovers of modern and contemporary art.
- Fulton Street (Fulton Street, lines 2, 3, 4, 5, A, C, J, Z). One of the busiest stations in Lower Manhattan, near the World Trade Center and Wall Street, frequented by commuters during the working week.